Characteristics of an Oligopoly
Characterized by interdependence, a relationship in which the outcome of each firm depends on the actions of the others
There are a "few" sellers in the market with significant control of pricing
If there are only two sellers, it's duopoly
Firms in an oligopoly have an incentive to collude, which is the act of "cooperating" or "not cheating" in order to increase joint profits
Cartel is a group of producers that agree to restrict output in order to increase prices and profits
Game Theory
The study of behavior in situations of interdependence is knowns as game theory
We will be examining a two-player model
- the x-player and the y-player (x,y)
In our pay off matrix, there will only be two possible choices
High/Low
Confess/Not Confess
Early/Late
Two firms are playing a "game" in which profits are dependent on other firms' actions
Applications in economics, military strategy, politics
John Nash, a mathematician, won the Nobel Prize in economics for his work
Nash equilibrium is the result when each player chooses the action that maximizes his or her payoff, given the actions of other players
Prisoner's Dilemma
Dominant strategy means that you will choose the same option regardless of what your opponents does
Prisoner's dilemma means that there exists a collusive outcome that will benefit both players but they will have a dominant strategy which will yield to the Nash Equilibrium of the lowest combined profit possible
Example 1 (classic)
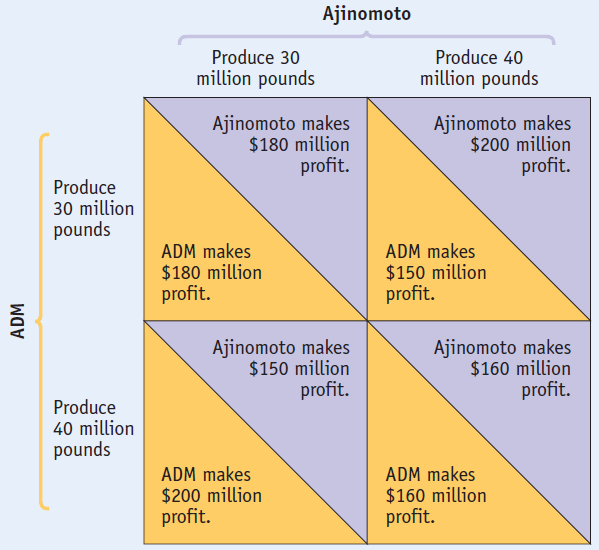
Two firms, ADM and Ajinomoto, must decide how much lysine to produce.
The profits of the two firms are interdependent: Each firm's profit depends not only on its own decision but also on the other's decision.
Both firms will be better off if they both choose the lower output
But it is in each firm's individual interest to choose the higher output.
Example 2 (One Dominant, One Not)
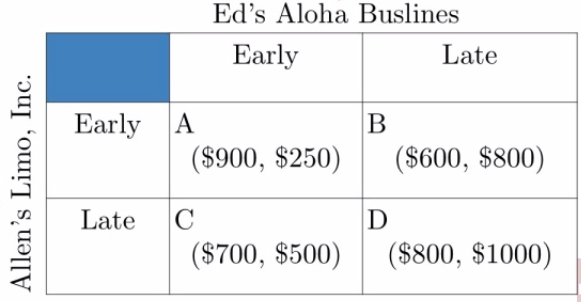
| Allen | Ed | |
|---|---|---|
| If early | Early | Late |
| If late | Late | Late |
| No dominant strategy | Late |
- Nash equilibrium: D
Overcoming prisoner's dilemma
Strategic behavior is when a firm attempts to influence the future behavior of other firms.
Tit for tat strategy involves playing cooperatively at first and then adjusting accordingly afterwards.
Firms in an oligopoly that do not explicitly form a cartel can engage in "tacit collusion" by limiting production and raising prices without any written agreements
Collusion, in any firm, is much more likely to take place when there are few firms
With more and more firms, there exists less incentive for a firm to "cheat"
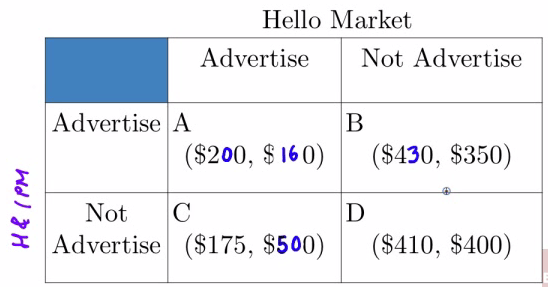
Example 3
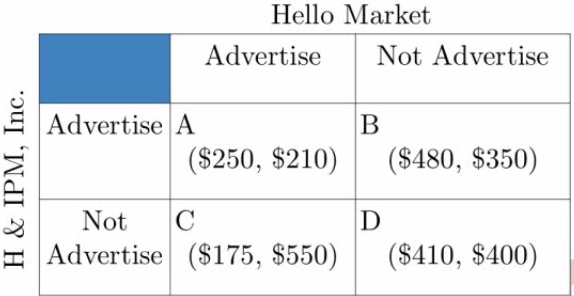
| Hello | H & IPM | |
|---|---|---|
| If advertise | Not advertise | Advertise |
| If not advertise | Advertise | Advertise |
| No dominant strategy | Advertise |
Does Hello Market have a dominant strategy?
- No
Does H & IPM have a dominant strategy?
- Yes, to advertise
At the Nash Equilibrium, what is H & IPM's daily profit? What is Hello Market's daily profit?
Choose B
H & IPM's daily profit: $480
Hello Market's daily profit: $350
Suppose the cost of advertising is $50 per day, redraw the matrix to include advertising costs for each firm